前言
对于从事后端开发的小伙伴来说,可能会遇到金额计算字段的类型,到底该用Long,还是BigDecimal的困扰。
甚至有些公司的架构师跟DBA,有时也会为了金额计算字段的类型而PK。
今天这篇文章专门跟大家一起聊聊这个话题,希望对你会有所帮助。
一、案发现场
有些小伙伴在工作中可能遇到过这样的场景:新来的开发小明负责公司电商平台的优惠券计算功能。
按照产品需求,满100减20的优惠券,用户下单金额是98.5元时,应该无法使用这张优惠券。
小明心想:这太简单了!
不到5分钟就写完了代码:
public class CouponService {public boolean canUseCoupon(double orderAmount, double couponThreshold) {return orderAmount >= couponThreshold;}public static void main(String[] args) {CouponService service = new CouponService();double orderAmount = 98.5;double couponThreshold = 100.0;boolean canUse = service.canUseCoupon(orderAmount, couponThreshold);System.out.println("订单金额" + orderAmount + "元,能否使用" + couponThreshold + "元门槛优惠券:" + canUse);// 输出:订单金额98.5元,能否使用100.0元门槛优惠券:true}
}
结果上线第一天,财务就炸锅了:大量本不该享受优惠的订单都被系统通过了,一天下来公司损失了3万多元!
小明百思不得其解:98.5明明小于100,为什么条件判断会出错呢?
二、浮点数的陷阱:计算机的小秘密
要理解这个问题,我们需要知道计算机是如何存储小数的。
2.1 二进制世界的局限
public class FloatProblemDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 看似简单的计算,却有问题double a = 0.1;double b = 0.2;double c = a + b;System.out.println("0.1 + 0.2 = " + c);System.out.println("0.1 + 0.2 == 0.3 ? " + (c == 0.3));// 让我们看看实际存储的值System.out.println("0.1的实际值: " + new BigDecimal(a));System.out.println("0.2的实际值: " + new BigDecimal(b));System.out.println("0.1+0.2的实际值: " + new BigDecimal(c));}
}
运行结果会让你震惊:
0.1 + 0.2 = 0.30000000000000004
0.1 + 0.2 == 0.3 ? false
0.1的实际值: 0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625
0.2的实际值: 0.200000000000000011102230246251565404236316680908203125
0.1+0.2的实际值: 0.3000000000000000444089209850062616169452667236328125
2.2 为什么会出现精度问题?
用一张图来理解浮点数的存储原理:
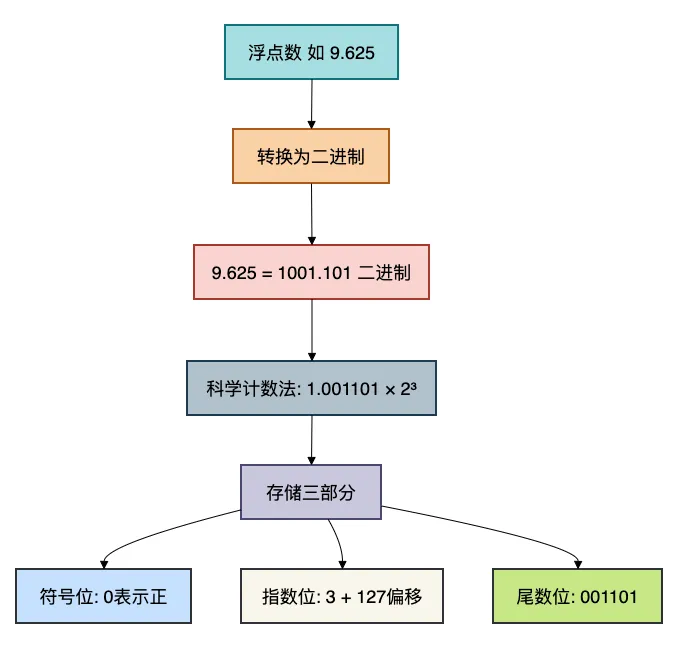
如何出现的问题?
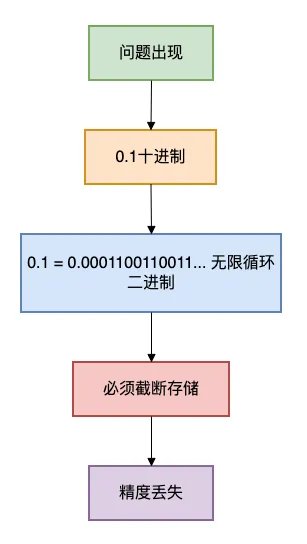
这就好比用1/3 ≈ 0.333333来表示三分之一,永远无法精确。
计算机的二进制系统也无法精确表示某些十进制小数。
三、两种解决方案的深度PK
面对金额计算的精度问题,Java开发者主要有两种选择。
让我们深入剖析每种方案的实现和原理。
3.1 方案一:货币使用Long
这种方法的核心思想:用分来计算,不用元。
public class MoneyWithLong {// 所有金额都以分为单位存储private Long amountInCents;public MoneyWithLong(Long amountInCents) {this.amountInCents = amountInCents;}// 加法public MoneyWithLong add(MoneyWithLong other) {return new MoneyWithLong(this.amountInCents + other.amountInCents);}// 减法public MoneyWithLong subtract(MoneyWithLong other) {return new MoneyWithLong(this.amountInCents - other.amountInCents);}// 乘法(处理折扣等场景)public MoneyWithLong multiply(double multiplier) {// 先将double转为整数分计算BigDecimal bd = BigDecimal.valueOf(multiplier).multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(this.amountInCents));return new MoneyWithLong(bd.longValue());}// 格式化显示public String display() {double yuan = amountInCents / 100.0;return String.format("%.2f元", yuan);}// 小明问题的正确解法public static boolean canUseCoupon(Long orderAmountInCents, Long thresholdInCents) {return orderAmountInCents >= thresholdInCents;}
}
实战场景:
public class LongSolutionDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 解决小明的问题Long orderAmount = 9850L; // 98.50元Long threshold = 10000L; // 100.00元boolean canUse = orderAmount >= threshold;System.out.println("订单98.5元能否使用100元门槛券: " + canUse);// 正确输出:false// 复杂计算示例MoneyWithLong price1 = new MoneyWithLong(1999L); // 19.99元MoneyWithLong price2 = new MoneyWithLong(2999L); // 29.99元MoneyWithLong total = price1.add(price2);System.out.println("总价: " + total.display()); // 49.98元// 折扣计算MoneyWithLong discounted = total.multiply(0.8); // 8折System.out.println("8折后: " + discounted.display()); // 39.98元}
}
3.2 方案二:BigDecimal精确计算
BigDecimal是Java提供的专门用于精确计算的类。
public class MoneyWithBigDecimal {private BigDecimal amount;private static final int SCALE = 2; // 保留2位小数private static final RoundingMode ROUNDING_MODE = RoundingMode.HALF_UP;public MoneyWithBigDecimal(String amount) {this.amount = new BigDecimal(amount).setScale(SCALE, ROUNDING_MODE);}public MoneyWithBigDecimal(BigDecimal amount) {this.amount = amount.setScale(SCALE, ROUNDING_MODE);}// 四则运算public MoneyWithBigDecimal add(MoneyWithBigDecimal other) {return new MoneyWithBigDecimal(this.amount.add(other.amount));}public MoneyWithBigDecimal subtract(MoneyWithBigDecimal other) {return new MoneyWithBigDecimal(this.amount.subtract(other.amount));}public MoneyWithBigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplier) {return new MoneyWithBigDecimal(this.amount.multiply(multiplier).setScale(SCALE, ROUNDING_MODE));}public MoneyWithBigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor) {return new MoneyWithBigDecimal(this.amount.divide(divisor, SCALE, ROUNDING_MODE));}// 比较public int compareTo(MoneyWithBigDecimal other) {return this.amount.compareTo(other.amount);}
}
BigDecimal的陷阱与正确用法:
public class BigDecimalCorrectUsage {public static void main(String[] args) {// 错误用法:使用double构造BigDecimal bad1 = new BigDecimal(0.1);System.out.println("错误构造: " + bad1);// 输出:0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625// 正确用法1:使用String构造BigDecimal good1 = new BigDecimal("0.1");System.out.println("String构造: " + good1);// 输出:0.1//正确用法2:使用valueOf方法BigDecimal good2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.1);System.out.println("valueOf构造: " + good2);// 输出:0.1// 除法的坑BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("10");BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("3");try {// 不指定精度会抛异常BigDecimal result = a.divide(b);} catch (ArithmeticException e) {System.out.println("必须指定精度: " + e.getMessage());}// 正确做法BigDecimal correctResult = a.divide(b, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);System.out.println("10 ÷ 3 = " + correctResult); // 3.33}
}
四、性能与存储的深度对比
有些小伙伴在工作中可能会问:两种方案性能差别大吗?对数据库有什么影响?
4.1 性能基准测试
public class PerformanceBenchmark {private static final int ITERATIONS = 10_000_000;public static void main(String[] args) {// Long方案性能long longStart = System.currentTimeMillis();long totalCents = 0L;for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {totalCents += 100L; // 1元totalCents -= 50L; // 0.5元totalCents *= 2;totalCents /= 2;}long longEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("Long方案耗时: " + (longEnd - longStart) + "ms");// BigDecimal方案性能long bdStart = System.currentTimeMillis();BigDecimal total = BigDecimal.ZERO;for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {total = total.add(new BigDecimal("1.00"));total = total.subtract(new BigDecimal("0.50"));total = total.multiply(new BigDecimal("2"));total = total.divide(new BigDecimal("2"), 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);}long bdEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("BigDecimal方案耗时: " + (bdEnd - bdStart) + "ms");System.out.println("性能差异倍数: " + (bdEnd - bdStart) * 1.0 / (longEnd - longStart));}
}
典型测试结果:
Long方案耗时: 25ms
BigDecimal方案耗时: 1250ms
性能差异倍数: 50.0
性能差距可达数十倍!这是为什么呢?
4.2 存储结构与原理分析
下面用几张图对比两种方案的存储:
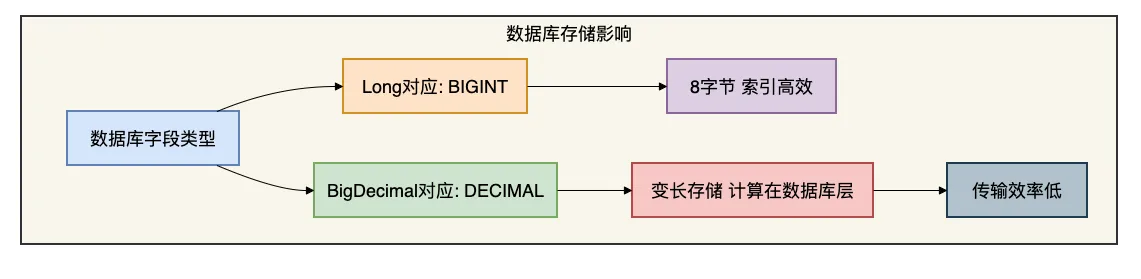
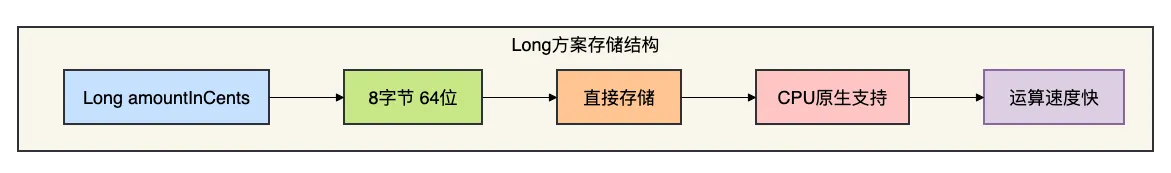
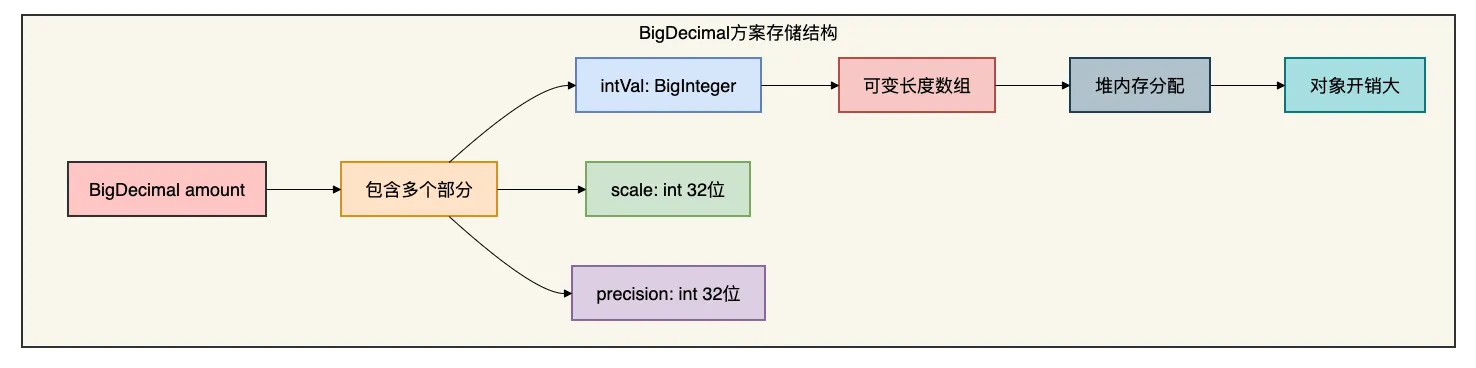
4.3 数据库层面的考虑
-- Long方案对应的表结构
CREATE TABLE orders_long (id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY,amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL, -- 以分为单位INDEX idx_amount (amount_cents) -- 索引效率高
);-- BigDecimal方案对应的表结构
CREATE TABLE orders_bd (id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY,amount DECIMAL(20, 2) NOT NULL, -- 总共20位,2位小数INDEX idx_amount (amount) -- 索引相对较大
);
数据库层面的差异:
- 存储空间:BIGINT固定8字节,DECIMAL是变长的
- 索引效率:BIGINT比较更快
- 跨数据库兼容性:BIGINT几乎所有数据库都支持且行为一致
- 计算位置:DECIMAL可以在数据库层计算,但业务逻辑通常应在应用层
五、真实业务场景深度分析
没有银弹,只有适合场景的方案。
5.1 场景一:金融交易系统(推荐Long)
// 银行核心系统示例
public class BankTransactionSystem {// 账户余额(单位:分)private AtomicLong balanceInCents = new AtomicLong();// 存款(线程安全)public boolean deposit(long cents) {if (cents <= 0) return false;balanceInCents.addAndGet(cents);return true;}// 取款(防止超取)public boolean withdraw(long cents) {while (true) {long current = balanceInCents.get();if (current < cents) return false;if (balanceInCents.compareAndSet(current, current - cents)) {return true;}// CAS失败,重试}}// 跨行转账(两阶段提交)public boolean transfer(BankTransactionSystem target, long cents) {if (!this.withdraw(cents)) {return false;}try {if (!target.deposit(cents)) {// 存款失败,回滚this.deposit(cents);return false;}return true;} catch (Exception e) {this.deposit(cents); // 异常回滚throw e;}}
}
为什么金融系统偏爱Long:
- 原子性操作:Java对long的原子操作支持完善(AtomicLong)
- 高性能:每秒数万笔交易必须考虑性能
- 精确无误差:分是最小单位,没有舍入问题
- 审计方便:所有操作都是整数,便于对账
5.2 场景二:电商优惠计算(BigDecimal更灵活)
public class EcommercePriceEngine {private BigDecimal price;// 复杂优惠计算public BigDecimal calculateFinalPrice(BigDecimal originalPrice,BigDecimal discountRate, // 折扣率BigDecimal fullReduction, // 满减BigDecimal coupon, // 优惠券boolean isVIP // VIP折扣) {BigDecimal result = originalPrice;// 折扣if (discountRate != null) {result = result.multiply(discountRate).setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);}// 满减if (fullReduction != null && result.compareTo(new BigDecimal("100")) >= 0) {result = result.subtract(fullReduction);}// 优惠券if (coupon != null) {result = result.subtract(coupon).max(BigDecimal.ZERO);}// VIP额外95折if (isVIP) {result = result.multiply(new BigDecimal("0.95")).setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);}return result;}// 分摊计算(如订单多个商品分摊优惠)public Map<String, BigDecimal> allocateDiscount(Map<String, BigDecimal> itemPrices,BigDecimal totalDiscount) {BigDecimal totalPrice = itemPrices.values().stream().reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);Map<String, BigDecimal> result = new HashMap<>();BigDecimal allocated = BigDecimal.ZERO;List<String> keys = new ArrayList<>(itemPrices.keySet());for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {String key = keys.get(i);BigDecimal price = itemPrices.get(key);// 按比例分摊BigDecimal ratio = price.divide(totalPrice, 10, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);BigDecimal itemDiscount = totalDiscount.multiply(ratio).setScale(2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);// 最后一个商品承担剩余金额if (i == keys.size() - 1) {itemDiscount = totalDiscount.subtract(allocated);}result.put(key, price.subtract(itemDiscount));allocated = allocated.add(itemDiscount);}return result;}
}
5.3 混合方案:鱼与熊掌兼得
有些复杂的系统会采用混合方案:
public class HybridMoneySystem {// 核心账户系统用Longprivate static class AccountCore {private long balanceCents; // 分单位public void transfer(AccountCore to, long cents) {// 高性能的整数运算this.balanceCents -= cents;to.balanceCents += cents;}}// 营销计算用BigDecimalprivate static class MarketingCalculator {public BigDecimal calculateCampaignEffect(BigDecimal budget,BigDecimal conversionRate,BigDecimal avgOrderValue) {// 复杂的浮点计算BigDecimal estimatedOrders = budget.multiply(conversionRate).divide(avgOrderValue, 4, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);return estimatedOrders.setScale(0, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);}}// 转换层public static long yuanToCents(BigDecimal yuan) {return yuan.multiply(new BigDecimal("100")).setScale(0, RoundingMode.HALF_UP).longValue();}public static BigDecimal centsToYuan(long cents) {return new BigDecimal(cents).divide(new BigDecimal("100"), 2, RoundingMode.UNNECESSARY);}
}
六、避坑指南
6.1 常见的坑
坑1:序列化问题
public class SerializationBug {// 使用默认序列化private BigDecimal amount;// 正确做法private transient BigDecimal amount; // 不自动序列化public String getAmountForJson() {return amount.toString(); // 明确转为String}public void setAmountFromJson(String amountStr) {this.amount = new BigDecimal(amountStr); // 明确从String构造}
}
坑2:等于判断的坑
public class EqualityBug {public static void main(String[] args) {BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("1.0");BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("1.00");System.out.println("a.equals(b): " + a.equals(b)); // false!System.out.println("a.compareTo(b): " + a.compareTo(b)); // 0// BigDecimal的equals不仅比较值,还比较scaleSystem.out.println("a.scale(): " + a.scale()); // 1System.out.println("b.scale(): " + b.scale()); // 2}
}
坑3:溢出问题
public class OverflowBug {public static void main(String[] args) {// Long的溢出long max = Long.MAX_VALUE;System.out.println("MAX: " + max);System.out.println("MAX + 1: " + (max + 1)); // 变成负数!// BigDecimal没有溢出,但可能性能问题BigDecimal huge = new BigDecimal(Long.MAX_VALUE);System.out.println("BigDecimal MAX * 2: " + huge.multiply(new BigDecimal("2"))); // 正确计算}
}
6.2 代码规范建议
// 金额处理的工具类
public final class MoneyUtils {private MoneyUtils() {} // 工具类私有构造// 全局统一的精度和舍入模式public static final int DEFAULT_SCALE = 2;public static final RoundingMode DEFAULT_ROUNDING = RoundingMode.HALF_UP;// 安全的创建方法public static BigDecimal safeCreate(String amount) {try {return new BigDecimal(amount).setScale(DEFAULT_SCALE, DEFAULT_ROUNDING);} catch (NumberFormatException e) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("无效金额: " + amount, e);}}// 转换方法public static long yuanToCents(BigDecimal yuan) {return yuan.multiply(new BigDecimal("100")).setScale(0, DEFAULT_ROUNDING).longValueExact(); // 精确转换,溢出抛异常}// 验证方法public static boolean isValidAmount(BigDecimal amount) {if (amount == null) return false;if (amount.scale() > DEFAULT_SCALE) return false;return amount.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) >= 0;}// 格式化显示public static String format(BigDecimal amount) {return String.format("¥%.2f", amount);}public static String format(long cents) {return String.format("¥%.2f", cents / 100.0);}
}
七、总结
文章最后跟大家总结一下。
7.1 选择原则
我画了一张图帮你做选择:
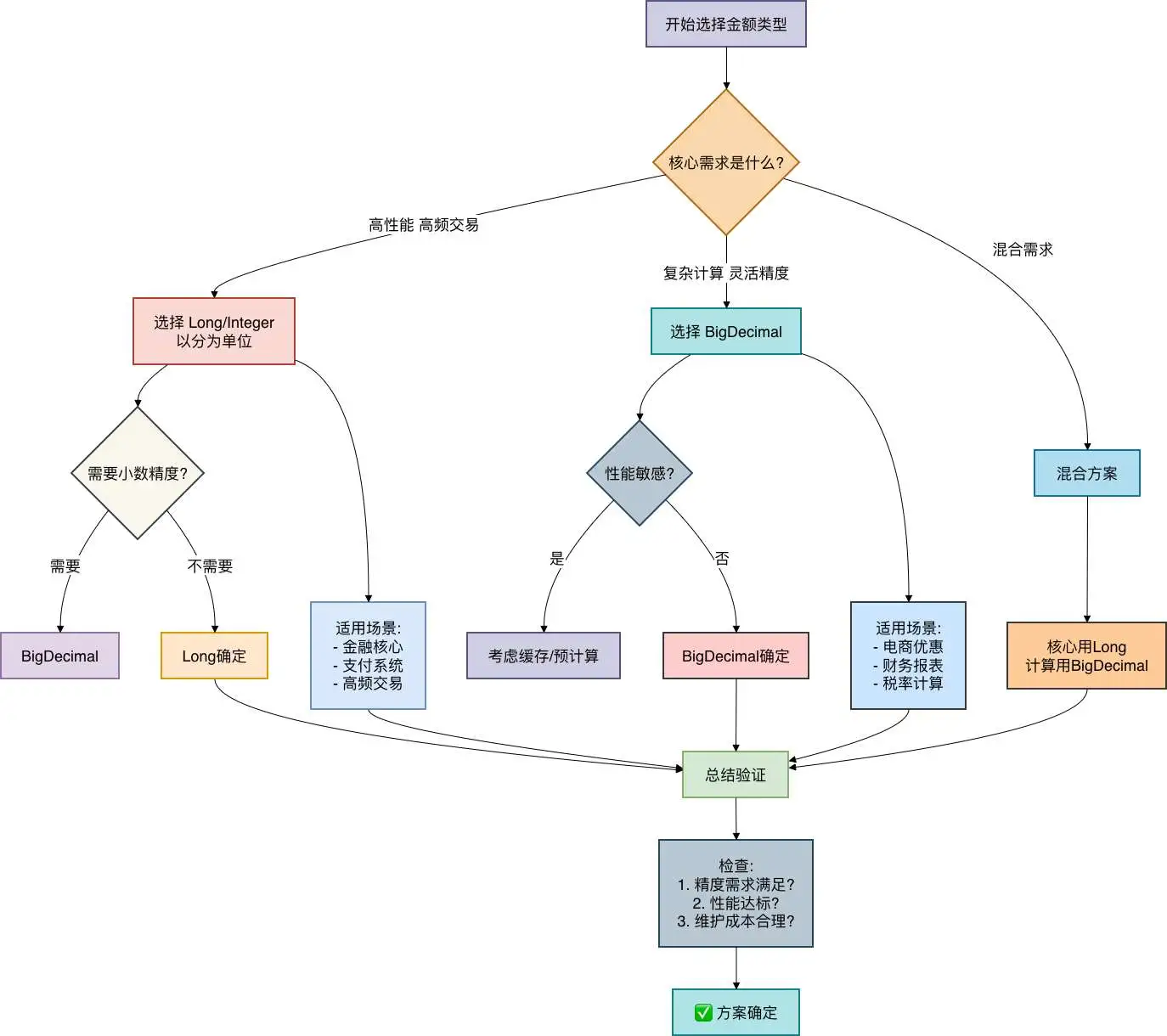
7.2 终极建议
-
金融核心系统:优先使用Long方案
- 支付、清算、账户余额等
- 理由:性能、原子性、一致性
-
电商营销系统:优先使用BigDecimal方案
- 优惠计算、价格引擎、促销活动
- 理由:灵活性、计算精度、业务变化快
-
混合型系统:采用分层架构
- 核心层用Long保证性能
- 计算层用BigDecimal保证精度
- 表现层做好格式化显示
7.3 最后的建议
记住这三条铁律:
- 金额计算无小事,必须严格测试
- 选择适合业务的技术,而不是最新的技术
- 保持一致性,一个系统内不要混用多种方案
技术选型就像选工具,用对了事半功倍,用错了后患无穷。
希望这篇文章能帮你在金额计算的路上少踩坑,走得更稳更远。
更多项目实战在我的技术网站:http://www.susan.net.cn/project
最后说一句(求关注,别白嫖我)
如果这篇文章对您有所帮助,或者有所启发的话,帮忙关注一下我的同名公众号:苏三说技术,您的支持是我坚持写作最大的动力。
求一键三连:点赞、转发、在看。
关注公众号:【苏三说技术】,在公众号中回复:进大厂,可以免费获取我最近整理的10万字的面试宝典,好多小伙伴靠这个宝典拿到了多家大厂的offer。