server块 与 虚拟主机
Nginx通过server块来定义虚拟主机,通过 listen和 server_name 来设置虚拟主机的端口和域名或IP。
server_name 指令用于匹配客户端请求的 Host 头字段,即请求设备发送的域名(或者IP地址)。
通过匹配 listen和server_name,Nginx 可以将请求路由到正确的 server 块。
为什么需要通过请求头
Host字段指定要请求的域名或者IP地址?(什么是虚拟主机)
- 同一IP托管多域名:当多个域名共享同一IP地址时,服务器依赖Host头区分不同网站,响应不同的服务(或者叫虚拟主机)。例如,example.com和test.com解析到同一IP,服务器通过Host头返回对应内容。适用于外部网站。
- 一块主机绑定多个IP地址,针对某个或某几个IP地址启用一个服务(或者叫虚拟主机),可以不互通。
- 不同的端口起不同的服务(或者叫虚拟主机)(通过
listen指令)适用于公司内部网站或外部网站的管理后台。- 必填字段:HTTP/1.1强制要求客户端发送Host头,否则服务器返回400 Bad Request
- Nginx默认行为:如果没有匹配到任何
server_name,Nginx 会选择第一个定义的server块作为默认服务器。
1. 配置基于域名的虚拟主机
server { listen 80; server_name www.example.com; location / { root /var/www/example; # root 指令用于指定静态资源的根目录。当客户端请求一个文件时,Nginx 会在这个目录下查找对应的文件。index index.html index.htm; # index 指令用于指定默认的索引文件。当客户端请求一个目录时(如 http://example.com/),Nginx 会按照 index 指令指定的文件顺序查找并返回第一个匹配的文件。}
}
这个配置定义了一个监听80端口的虚拟主机,域名为www.example.com。根目录设置为/var/www/example,默认页面为index.html或index.htm。
静态网站部署
root /var/www/example; # root 指令用于指定静态资源的根目录。当客户端请求一个文件时,Nginx 会在这个目录下查找对应的文件。 index index.html index.htm; # index 指令用于指定默认的索引文件。当客户端请求一个目录时(如 http://example.com/),Nginx 会按照 index 指令指定的文件顺序查找并返回第一个匹配的文件。
2. 配置基于IP的虚拟主机
- 首先,需要在服务器上配置多个IP地址。
- 然后,在Nginx配置文件中为每个IP地址定义一个
server块。
server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.1.100; location / { root /var/www/ip1; index index.html index.htm; }
} server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.1.101; location / { root /var/www/ip2; index index.html index.htm; }
}
3. 配置基于端口的虚拟主机
- 在同一个IP地址上,通过不同的端口来区分不同的虚拟主机。
server { listen 8080; server_name localhost; location / { root /var/www/port8080; index index.html index.htm; }
} server { listen 8090; server_name localhost; location / { root /var/www/port8090; index index.html index.htm; }
}
location
默认的根目录 /
server {listen 80;server_name localhost;location /tomcat {proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;# proxy_pass http://tomcat-travel;}}
这个时候没有配置根目录,如果访问http://localhost:80,依然会显示nginx的欢迎页面
所以 下面的location就是默认就有的。
location / {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}
location支持正则表达式匹配(匹配请求的URL)
使用不同正则表达式编写的规则,满足多条规则的同一url有不同的处理优先级。
location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}location = / {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107 结果test1
location = / {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107 结果test1
= / 的优先级低于 /
location = /test/page/ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/test/page/ html
location = /images/ {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/images/ html
= /test/page/ 的优先级低于 /
location = /images/ {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}
location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/images/ test1
/test/ 的优先级高于 /
location = /test/ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}
location = /test/page/ {root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}
location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}http://106.15.129.107/test/page/ test4
/test/page/ 的优先级高于 /test/
location = ^~ /images/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
location = / {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}
location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/images/index.html test2
location = / {root html;index index.html index.htm;
}
location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}
location = ^~ /images/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/images/index.html test2
^~ 的优先级高于 /test/page/
location ^~ /test/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/test/index.html test2
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}location ^~ /test/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/test/index.html test2
^~ 的优先级高于 ~
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}location ~* .*\.(html)$ {root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/test/index.html test3
location ~* .*\.(html)$ {root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}
106.15.129.107/test/index.html test4
~的优先级等于~* ,按照从上往下配置顺序,匹配第一个规则
location ~* .*\.(html)$ {root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}
location /test/page/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
106.15.129.107/test/page/index.html test4
location /test/page/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~* .*\.(html)$ {root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(html)$ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}
106.15.129.107/test/page/index.html test4
~*和~的优先级高于/test/page/
location /test/page/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
location = /test/page/ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}106.15.129.107/test/page/ test2
location = /test/page/ {root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}
location /test/page/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}
106.15.129.107/test/page/ test2
= /test/page/的优先级低于/test/page/
# 匹配以 /images/ 开头的请求,停止正则匹配
location ^~ /test/ { # ^~ 普通字符串匹配,匹配成功后停止正则匹配。root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}# ~* 和 ~ 优先级一致,同时配置时,按照从上到下第一个配置执行location ~* .*\.(html)$ { # ~* 不区分大小写的正则匹配。root test4;index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(html)$ { # ~ 区分大小写的正则匹配。root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}location /test/page/ {root test2;index index.html index.htm;
}location /test/ { # 普通字符串前缀匹配:匹配以 /images/ 开头的请求root test3;index index.html index.htm;
}location / {root test1;index index.html index.htm;
}location = /images/ { # 精确匹配:# 仅匹配root html;index index.html index.htm;
}
内部跳转:使用 @ 修饰符,用于 Nginx 内部跳转。
Nginx内置变量
以 http://188.19.236.18:8000/abc?test=123&test2=abc 为例子,其中:
$args:test=123&test2=abc
$uri: /abc
$server_addr:188.19.236.18
$server_port:8000
$request_filename:abc
$request_uri:/abc?test=123&test2=abc
例2: http://172.16.213.199:88/test1/test2/test.php ,假定虚拟主机根目录为/var/www/html,其中:
$host:172.16.213.199
$server_port:88
$request_uri: /test1/test2/test.php
$document_uri:/test1/test2/test.php
$document_root:/var/www/html
$request_filename:/var/www/html/test1/test2/test.php
处理请求
if指令
(1) 基本功能
- 作用:
if用于判断条件,若条件成立,则执行大括号内的配置指令,未提及的配置会继承自上级(如server或location块)。 - 语法:
if (condition) { # 配置指令 } - 使用范围:只能在
server或location块中使用。
(2) 条件类型
支持以下两类条件判断:
-
正则表达式匹配:
~:区分大小写的正则匹配(如if ($uri ~ "\.jpg$"))。~*:不区分大小写的正则匹配(如if ($http_user_agent ~* "Mobile"))。!~/!~*:反向匹配(如if (!~ "\.css$"))。
-
文件/目录检测:
-f/!-f:判断文件是否存在(如if (-f $request_filename))。-d/!-d:判断目录是否存在。-e/!-e:判断文件或目录是否存在。-x/!-x:判断文件是否可执行。
location / {if ($query_string ~ "id=(\d+)") {set $id $1;rewrite ^/app.php$ /m-$id.html? last;}
}
rewrite指令
Nginx通过ngx_http_rewrite_module模块支持url重写、支持if条件判断,但要使用rewrite功能,需要PCRE支持,应在编译nginx时指定PCRE源码目录。
使用字段:server, location, if
1. 基本语法
rewrite regex replacement [flag];
- 参数说明:
regex:正则表达式,用于匹配请求的URL路径(不包含查询参数?xxx)。replacement:匹配成功后,要替换成的新URL路径(可包含捕获组$1、$2等)。flag:可选标记,控制重写行为,常见的标记包括:last:停止当前rewrite规则匹配,重新搜索新的location块。break:停止rewrite规则匹配,使用当前重写后的URL继续处理。redirect:将返回302临时重定向,在浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址。permanent:将返回301永久重定向,在浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址。- 其中,last和break用来实现URL重写,浏览器地址栏中的URL地址不变。
| 标志 | 作用 | 浏览器地址栏变化 | 常用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
last |
停止当前rewrite规则,重新匹配location块(类似Apache的[L]) |
无变化 | 内部跳转、路径调整 |
break |
停止rewrite规则匹配,使用当前URL继续处理(不重新匹配location) |
无变化 | 简单替换后直接处理 |
redirect |
返回302临时重定向响应 | 发生跳转 | 临时迁移页面 |
permanent |
返回301永久重定向响应 | 发生跳转 | 永久迁移页面或SEO优化 |
客户端请求 http://example.com → Nginx直接返回301跳转 → 客户端请求 https://example.com ,无需触达Java应用。
break 表示完成当前设置的规则后,不再匹配后面的重写规则。
server {listen80;server_name www.tb.cn;if ($host != 'www.tb.cn') {rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.tb.cn/error.txtbreak;rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.tb.cn/$1 permanent;}
}
location ~ ^/new/ {rewrite ^/new/(.*)$ /old/$1 break;proxy_pass http://www.tb.com;
}
注意事项
- 正则表达式匹配顺序 当有多个
rewrite规则时,Nginx会按照配置文件中的顺序进行匹配,后匹配的规则可能覆盖前面的规则。所以要注意规则的顺序,避免出现意外的匹配结果。 - 性能影响 过度复杂的
rewrite规则可能会影响Nginx的性能。在实际应用中,尽量保持规则简单明了,避免使用非常复杂的正则表达式。
return指令
- 当客户端访问
http://example.com/old时,服务器会返回301状态码,并在Location头信息中包含http://example.com/new,浏览器收到这个响应后,会自动跳转到新的URL。
可以在Nginx配置文件的server块中添加如下配置:
server{listen 80;server_nameexample.com;location /old-path{return 301 http://example.com/new-path;}
}
- 语法:
return code \[text\];或者return code URL;。其中code是HTTP状态码,常见的有301(永久重定向)、302(临时重定向)等。text是可选的响应体内容(如果不重定向到URL的话),URL是要重定向到的目标URL。
set指令
通过set指令可以设置一个变量并为其赋值,其值可以是文本、变量或它们的组合。也可以使用set定义一个新的变量,但是不能使用set设置$http_xxx头部变量的值。
1. set指令的核心功能
- 作用:
set用于定义或赋值变量,可以将文本、现有变量或它们的组合赋值给一个新变量。 - 语法:
set $variable_name value;$variable_name:自定义变量名(以$开头)。value:可以是文本、现有变量或两者的组合(如$arg_id-$suffix)。
- 使用范围:
可在server、location、if块中使用。
2. 示例配置解析
location / {if ($query_string ~ "id=(.*)") {set $myid $1;rewrite ^/app.php$ /m-$myid.html?;}
}
执行流程分析:
- 条件判断:
当请求的查询参数($query_string)中包含id=时(如/app.php?id=100),进入if块。 - 变量赋值:
- 使用正则表达式捕获
id的值((.*)),并赋值给变量$myid。 - 例如,请求
id=100时,$myid的值为100。
- 使用正则表达式捕获
- URL重写:
- 将请求
/app.php重写为/m-$myid.html(如/m-100.html)。 ?结尾的作用是清除原始查询参数,避免新URL携带旧参数(如/m-100.html?id=100)。
- 将请求
3. 关键特性与注意事项
-
作用域:
set定义的变量仅在当前配置块内有效(如server、location或if块)。 -
不可设置HTTP头变量:不能通过
set修改$http_xxx类变量(如$http_user_agent)。set $http_user_agent "Custom-Agent"; # ❌ 无效,HTTP头变量需用`proxy_set_header`设置 -
变量名冲突:若变量已存在,
set会覆盖其值。set $myvar "old"; if ($arg_id) {set $myvar "new_$arg_id"; # 覆盖原值 }
测试
在将重定向规则应用到生产环境之前,最好在测试环境中进行充分的测试,确保重定向的行为符合预期。可以使用工具如curl来模拟请求,检查返回的状态码和重定向的目标URL是否正确。例如,使用curl -I http://example.com/old-path可以查看请求http://example.com/old-path时返回的头信息,包括重定向状态码和目标URL。
Nginx 日志
Nginx 日志分为 访问日志 和 错误日志 两种,分别记录客户端的请求信息和服务器运行中的错误信息。
访问日志(access_log)
- 作用:记录客户端访问 Nginx 的每一个请求,包括请求的详细信息、处理结果等。
- 配置:
- 使用
log_format指令定义日志格式。 - 使用
access_log指令指定日志文件路径和格式。
- 使用
- 示例配置:
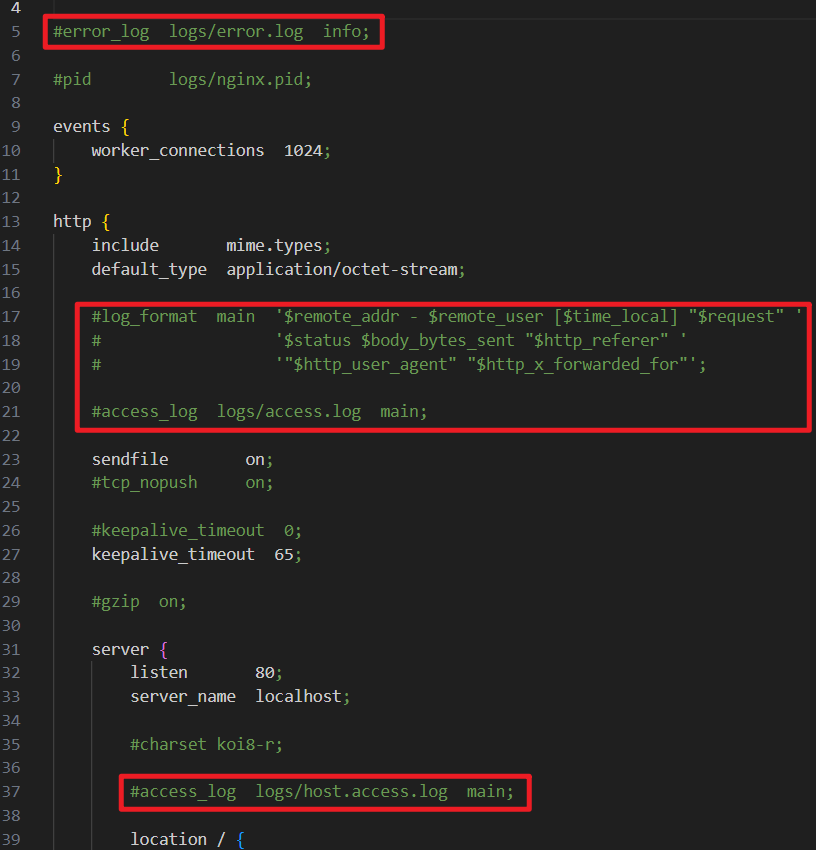
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log logs/access.log main;access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]];access_log off;
$uri请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数,参数位于$args),不同于浏览器传递的$request_uri的值,它可以通过内部重定向,或者使用index指令进行修改。不包括协议和主机名,例如/foo/bar.html。
$request_uri 这个变量等于包含一些客户端请求参数的原始URI,它无法修改,请查看$uri更改或重写URI。
也就是说:$request_uri是原始请求URL,$uri则是经过nginx处理请求后剔除参数的URL,所以会将汉字表现为union。
坑点:
使用$uri 可以在nginx对URL进行更改或重写,但是用于日志输出可以使用$request_uri代替,如无特殊业务需求,完全可以替换。
- 日志缓存:
- 使用
open_log_file_cache缓存日志文件描述符,减少频繁打开/关闭日志文件的性能开销。
open_log_file_cache max=1000 inactive=20s valid=1m min_uses=2;- max:设置缓存中的最大文件描述符数量,如果缓存被占满,采用LRU算法将描述符关闭。
- inactive:设置存活时间,默认是10s
- min_uses:设置在inactive时间段内,日志文件最少使用多少次后,该日志文件描述符记入缓存中,默认是1次
- valid:设置检查频率,默认60s
- off:禁用缓存
- 使用
错误日志(error_log)
- 作用:记录 Nginx 运行过程中遇到的错误信息,包括服务器错误和请求处理错误。
- 配置:
error_log logs/error.log info; - 日志级别(从低到高):
debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit、alert、emerg。