文章目录
- 前言
- 一、二叉树链式结构的实现
- 1、统计二叉树结点个数
- (1)、用局部变量进行统计
- (2)、用全局变量进行统计
- (3)、给结构体加一个变量
- 给函数添加一个新的变量size进行统计
- (4)递归实现(最优)
- 2、二叉树叶子结点个数
- 3、二叉树第K层节点个数
- 4、二叉树的高度
- 5、二叉树查找值为x的结点
- 6、二叉树的销毁
- 7、总代码
- 二、二叉树层序遍历的实现
- 三、深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS)
- 1、深度优先遍历(DFS, Depth-First Search)
- 核心概念
- 工作原理与分类
- 示例(二叉树结构)
- 实现方式
- 2、广度优先遍历(BFS, Breadth-First Search)
- 核心概念
- 工作原理
- 示例(同上二叉树结构)
- 实现方式
- 总结:DFS与BFS的关键区别
- 四、判断是否为完全二叉树
- 五、总代码(包括队列的代码)
- 队列相关代码
- Queue.h
- Queue.c
- 二叉树
- Tree.h
- Tree.c
- test.c
- 六、结束语
个人主页:星轨初途
个人专栏:C语言,数据结构
前言
嗨٩(๑❛ᴗ❛๑)۶,我们又见面啦,上一篇我们了解到二叉树链式结构的概念及二叉树遍历方式,数据结构二叉树之链式结构(3)(上),今天我们就来继续了解二叉树的的相关功能以及实现,让我们一起来了解它吧!
本篇相关的知识点,需要的自取
传送门:
栈与队列核心篇(下):从基础到进阶,玩转队列设计
栈与队列核心篇(上):从原理到代码,吃透栈结构
数据结构之初识二叉树(1)——核心概念入门
数据结构二叉树之链式结构(3)(上)
一、二叉树链式结构的实现
我们上一篇已经手动构造了一个链式二叉树,这里就不再讲啦
#include<stdio.h>typedef int BTDataType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(int x){BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;}BTNode* CreatBinaryTree(){BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;return node1;}int main(){BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();return 0;}图相
1、统计二叉树结点个数
我们想统计二叉树的节点个数,我们第一时间就想到定义一个变量size来遍历进行查找
(1)、用局部变量进行统计
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
int size = 0;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
++size;
TreeSize(root->left);
TreeSize(root->right);
return size;
}我们不用看结果就知道size为0,因为每次调用都会被初始化,那我们可以尝试把它变成全局变量
(2)、用全局变量进行统计
int size = 0;
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
++size;
TreeSize(root->left);
TreeSize(root->right);
return size;
}或者
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
static int size = 0;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
++size;
TreeSize(root->left);
TreeSize(root->right);
return size;
}这两个效果一样,我们来验证一下
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
return 0;
}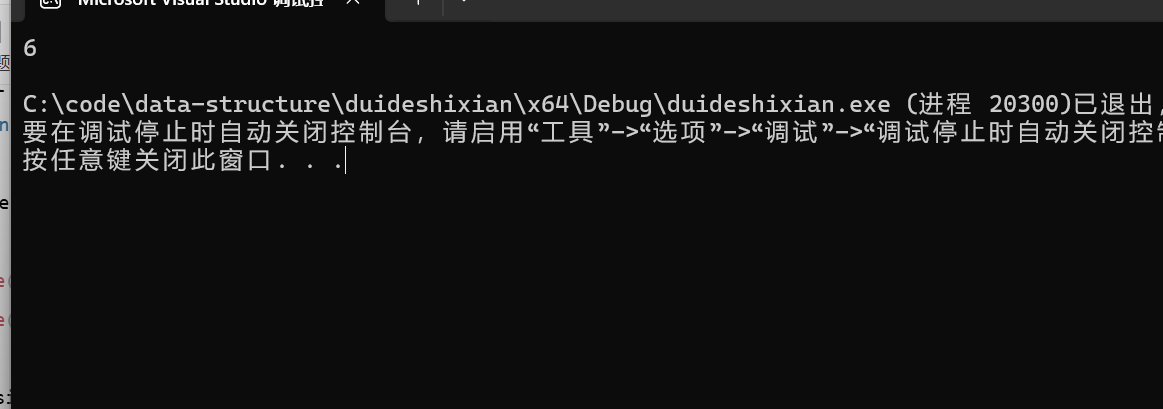
结果,好像也对,但是我们再调用一次呢
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
return 0;
}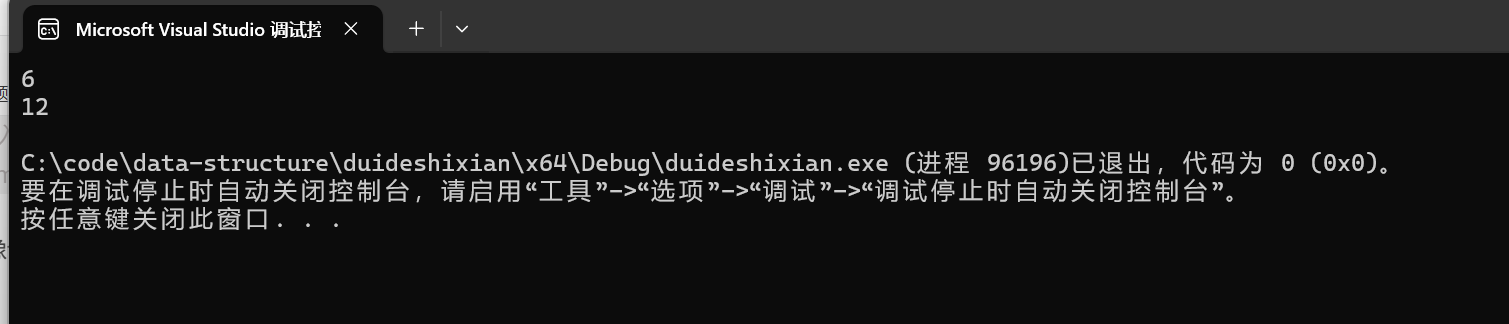
我们发现因为全局变量,导致第二次重复加了,我们该怎么解决呢
(3)、给结构体加一个变量
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
int size;
}BTNode;这样会大大扩大二叉树所占的空间,并不划算,那有没有更好的方法呢?
给函数添加一个新的变量size进行统计
void TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
++(psize);
TreeSize(root->left, psize);
TreeSize(root->right, psize);
}
int main()
{
int size = 0;
TreeSize(root, size);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n",size);
return 0;
}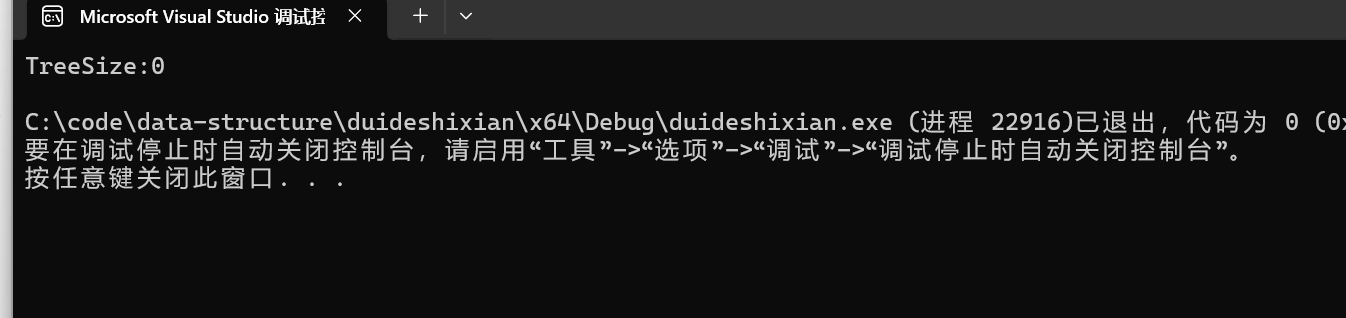
为什么是0呢?
哦~,原来要传地址才能改变size的值
所以我们进行改正
void TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
++(*psize);
TreeSize(root->left, psize);
TreeSize(root->right, psize);
}
int main()
{
int size = 0;
TreeSize(root, &size);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n",size);
return 0;
}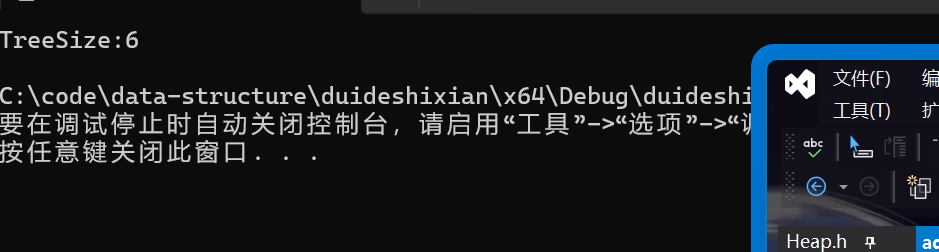
正确
调用两回,需要重新初始化
int main()
{
int size = 0;
TreeSize(root, &size);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n",size);
size = 0;
TreeSize(root, &size);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n", size);
return 0;
}每次初始化很麻烦,我们还有没有其他简单的方法?有的
(4)递归实现(最优)
如果不创建新的变量,用递归实现,遍历二叉树,若为空返回0,非空返回1(自己)+左右两个子树的节点个数
代码如下:
//二叉树结点个数 = 1 + 左子树结点个数 + 右子树结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == 0)
{
return 0;
}
return 1 + TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
return 0;
}结果
正确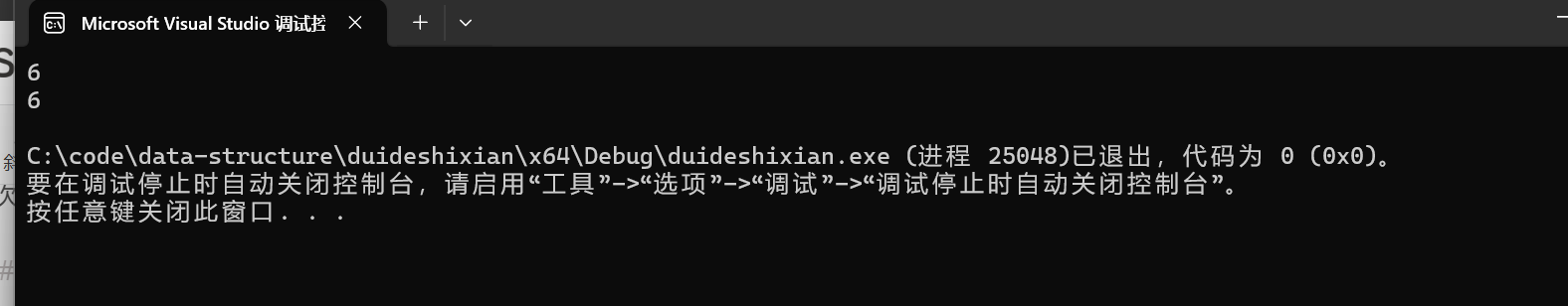
2、二叉树叶子结点个数
思路
这里我们还是用递归来写
如果左右子节点都为NULL,就证明是叶子节点,返回1
如果该节点为NULL空节点,返回0,
除此就是不是叶子了,返回左子树+右子树的节点数之和
代码
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left)
+ TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
printf("%d\n", TreeLeafSize(root));
return 0;
}结果,结合图形我们知道正确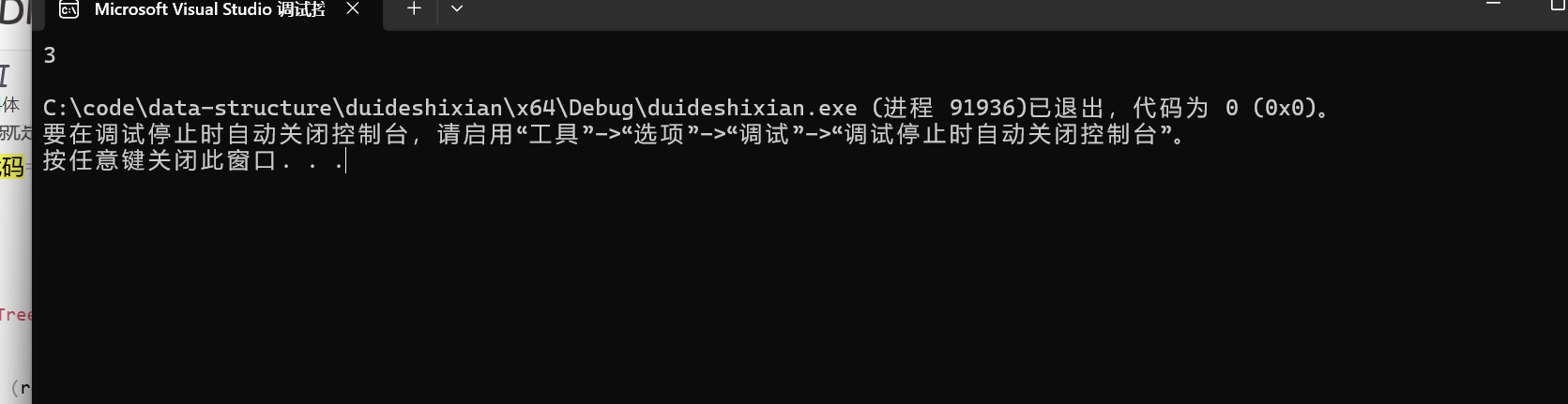
3、二叉树第K层节点个数
我们还递归遍历,但我们怎么知道遍历到了第K层了呢,我们只需要再把k-1传到函数中,当k减到1时就是我们需要的那一层
如当k=3时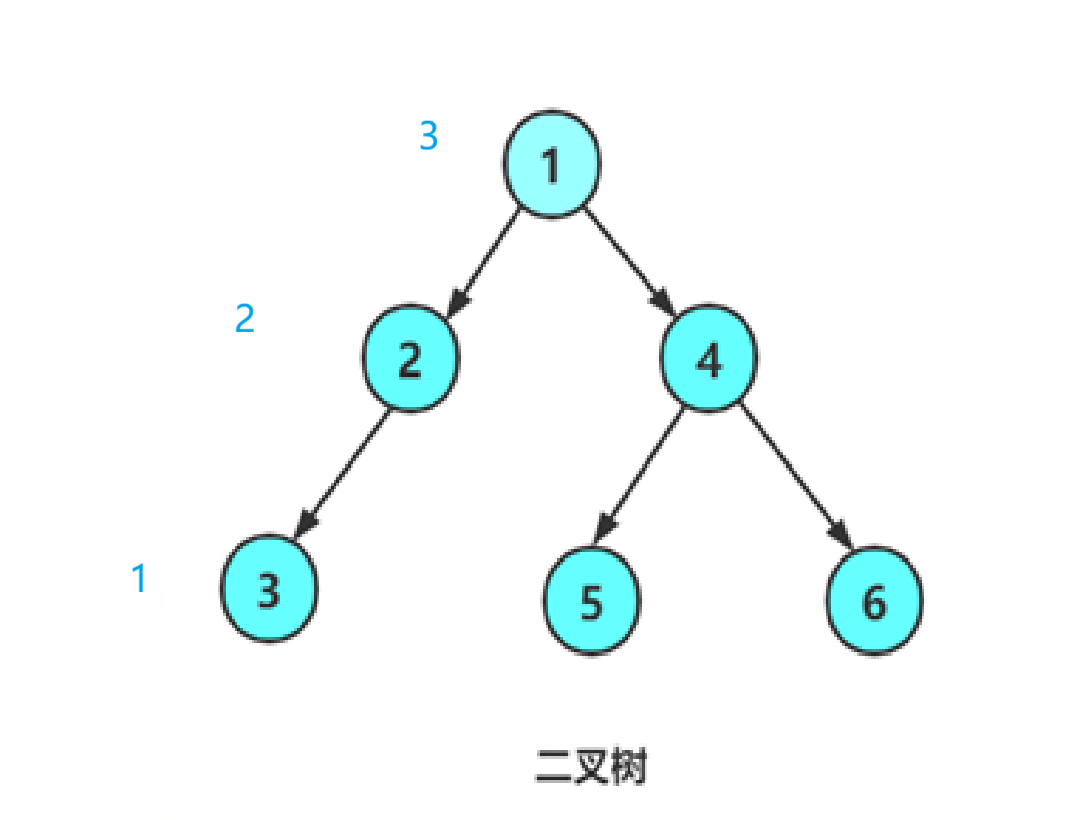
代码
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
// 子问题
return TreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1)
+ TreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
int k;
scanf("%d",&k);
printf("%d\n", TreeLevelKSize(root,k));
return 0;
}结果
4、二叉树的高度
求二叉树的高度,就是看最高的一条,也就是本身节点加上左右树中高度高的那个
用代码实现
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return TreeHeight(root->left) > TreeHeight(root->right) ?
TreeHeight(root->left) + 1 : TreeHeight(root->right) + 1;
}而这个代码最后返回时先比较再决定返回哪个,但是因为没有保存数值,还要再算一次,递归到子树子树也会再算一次,会导致多次运算,超时,所以我们把数值进行保存
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ?
leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
printf("%d\n", TreeHeight(root));
return 0;
}结果与我们构造的二叉树高度一致,功能正常实现
5、二叉树查找值为x的结点
我们要找值为x的节点,我们分别进行左树右树进行查找,左树找到返回该节点,没有进行右树查找从根节点开始。按 “当前节点→左子树→右子树” 的顺序搜索值为x的节点,找到则返回该节点的指针,遍历完整棵树仍未找到则返回NULL。
代码如下
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
BTNode* find = TreeFind(root, 6);
if (find)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");
BTNode* fin = TreeFind(root, 7);
if (fin)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");
return 0;
}代码实现正确
6、二叉树的销毁
// 二叉树销毁
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
TreeDestory(root);
root = NULL;
return 0;
}最后主函数再让root=NULL就行啦,在调用函数无法置空,要想置空修改原指针的值,得传地址,需要改为二级指针
// 二叉树销毁
void TreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{
if (*root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestory(&((*root)->left));
TreeDestory(&((*root)->right));
free(*root);
*root = NULL;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
TreeDestory(&root);
return 0;
}两个都可以只不过
第一个需要手动置空,但比较简洁
第二个需要额外置空,传地址,但是更彻底
7、总代码
头文件
Tree.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedef int BTDataType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;}BTNode;//前序遍历void PerOrder(BTNode* root);//中序遍历void InOrder(BTNode* root);//后序遍历void PostOrder(BTNode* root);//二叉树结点个数 int TreeSize(BTNode* root);//void TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize);//二叉树叶子结点个数 int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);//二叉树第k层结点个数 int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);//二叉树的高度int TreeHeight(BTNode* root);//二叉树查找值为x的结点 BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);// 二叉树销毁void TreeDestory(BTNode** root);功能实现
Tree.c
#include"Tree.h"
//前序遍历
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
//二叉树结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//二叉树叶子结点个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left)
+ TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
// 子问题
return TreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1)
+ TreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
//二叉树的高度
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ?
leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
// 二叉树销毁
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
//// 二叉树销毁
//void TreeDestory(BTNode** root)
//{
// if (*root == NULL)
// {
// return;
// }
// TreeDestory(&((*root)->left));
// TreeDestory(&((*root)->right));
// free(*root);
// *root = NULL;
//}测试
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Tree.h"
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
//BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node5->right = node7;
return node1;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
/*printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));*/
/*printf("%d\n", TreeLeafSize(root));
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);
printf("%d\n", TreeLevelKSize(root, k));
printf("%d\n", TreeHeight(root));
BTNode* find = TreeFind(root, 6);
if (find)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");
BTNode* fin = TreeFind(root, 7);
if (fin)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");*/
TreeDestory(root);
return 0;
}二、二叉树层序遍历的实现
层序遍历:除了先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历外,还可以对二叉树进行层序遍历。设二叉树的根结点所在层数为1,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根结点出发,首先访问第一层的树根结点,然后从左到右访问第2层上的结点,接着是第三层的结点,以此类推,自上而下,自左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历
简单来说,就是从上到下一层一层看
如图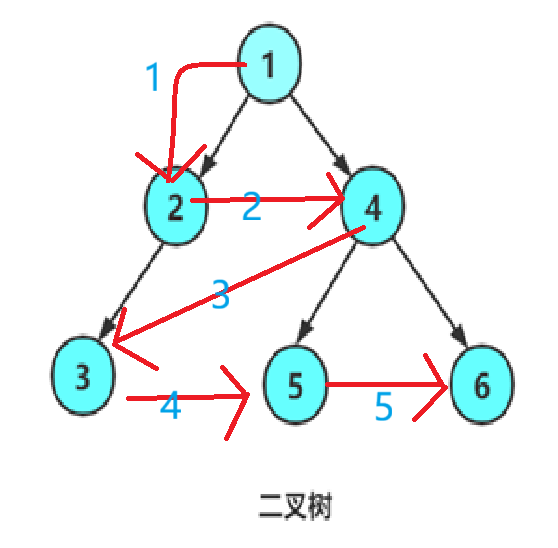
而这肯定不能用递归实现,那我们怎么实现呢?
这时我们想到可以用队列呀!我们前面讲了队列的实现,我们可以用队列的功能来实现,怎么实现呢?
如下图,头节点进去,出队列时让子节点入队列,反复操作就完成了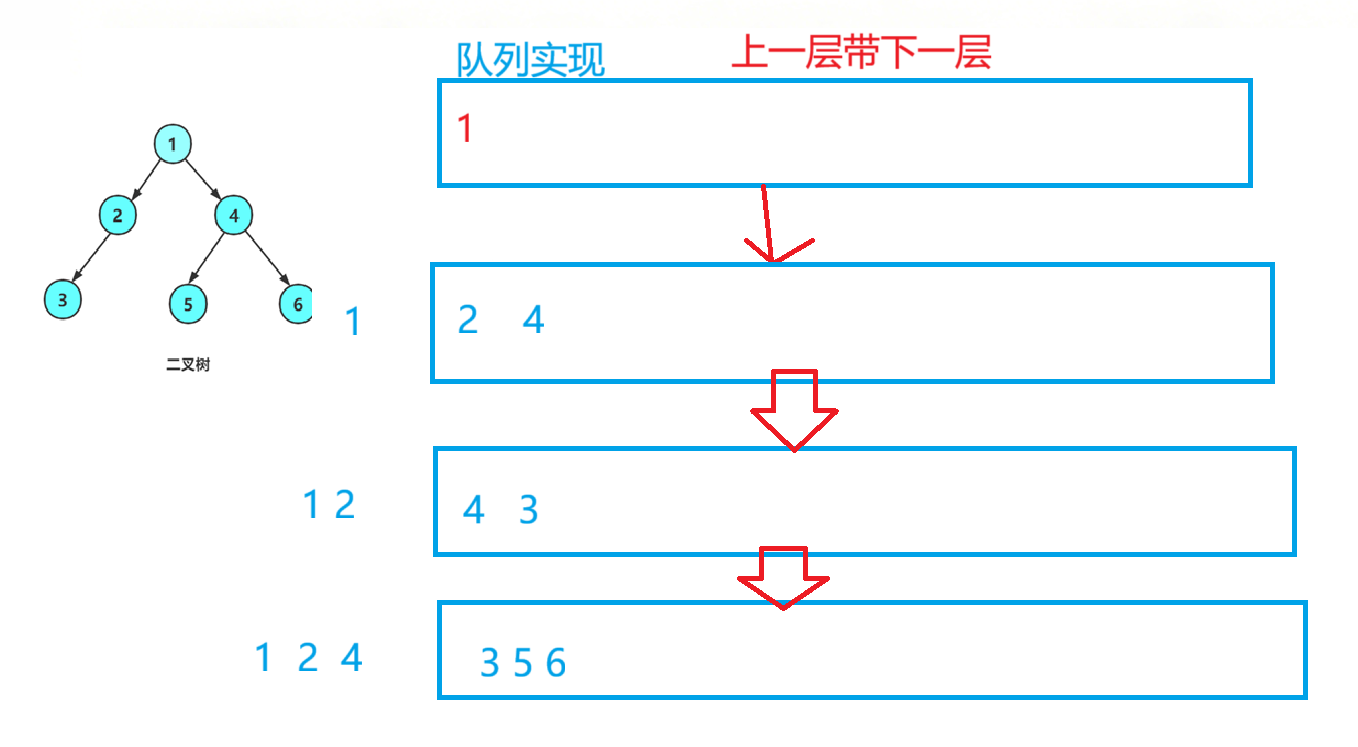
这时我们需要用到队列的代码,我们再讲队列时已经把队列的代码放在文章中啦,所以这里我们直接 添加–>现有项
找到对应文件添加
或者直接建新建项把代码Ctrl+v过来
传送门:栈与队列核心篇(下):从基础到进阶,玩转队列设计(可以在这篇文章最后找)
就把文件过来了,在实现前
好啦,我们现在来实现二叉树的层序遍历
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
TreeLevelOrder(root);
TreeDestory(root);
return 0;
}结果,正确实现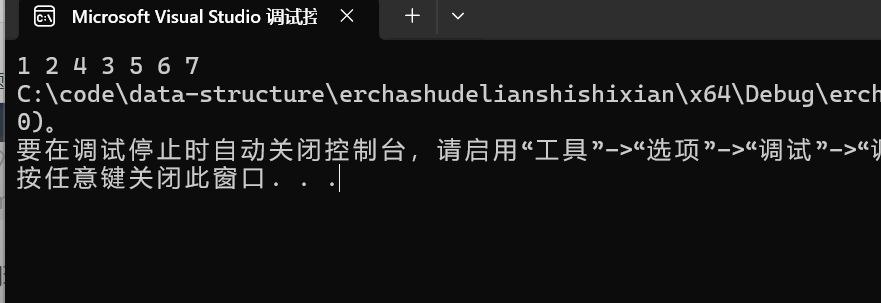
三、深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS)
前面前中后序都是深度优先遍历,层序遍历就是广度优先遍历
1、深度优先遍历(DFS, Depth-First Search)
核心概念
深度优先遍历是沿着二叉树的深度方向探索,优先走到某一分支的最深处,遇到叶子节点(无法再深入)后再回溯,继续探索其他未走完的分支。简单说就是“一条路走到黑,回头再走其他路”。
工作原理与分类
在二叉树中,DFS根据“访问根节点”的时机不同,分为三种具体形式(以根节点N、左子树L、右子树R表示):
- 前序遍历(N→L→R):先访问根节点 → 递归遍历左子树 → 递归遍历右子树;
- 中序遍历(L→N→R):先递归遍历左子树 → 访问根节点 → 递归遍历右子树;
- 后序遍历(L→R→N):先递归遍历左子树 → 递归遍历右子树 → 访问根节点。
示例(二叉树结构)
1/ \2 3/ \
4 5- 前序遍历结果:1 → 2 → 4 → 5 → 3;
- 中序遍历结果:4 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 3;
- 后序遍历结果:4 → 5 → 2 → 3 → 1。
实现方式
通常用递归(代码简洁)或栈(模拟递归过程,避免栈溢出)实现。比如你之前看到的二叉树查找代码,本质就是前序遍历的DFS。
2、广度优先遍历(BFS, Breadth-First Search)
核心概念
广度优先遍历(也叫层序遍历)是按二叉树的层次顺序遍历:先访问根节点所在的第一层,再访问第二层的所有节点,接着第三层……依此类推,同一层内按“左→右”顺序访问。简单说就是“一层一层往下扫”。
工作原理
依赖队列(先进先出)实现:
- 根节点入队;
- 队首节点出队并访问;
- 将出队节点的左孩子、右孩子依次入队(若存在);
- 重复步骤2-3,直到队列为空。
示例(同上二叉树结构)
层序遍历结果:1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5(第一层→第二层→第三层)。
实现方式
必须用队列(或数组模拟队列)实现,无法用简单递归(递归天然偏向深度)。
总结:DFS与BFS的关键区别
| 特性 | 深度优先遍历(DFS) | 广度优先遍历(BFS) |
|---|---|---|
| 遍历顺序 | 深度优先,先探分支尽头 | 广度优先,先扫完一层 |
| 数据结构 | 递归(隐式栈)或显式栈 | 队列 |
| 适用场景 | 找路径、计算深度、前/中/后序操作 | 层序操作、找最短路径(如二叉树最小深度) |
| 空间复杂度(最坏) | 取决于树的深度(如链状树O(n)) | 取决于树的最宽层节点数(如满二叉树O(n)) |
简单记:DFS是“钻洞”,BFS是“扫面”——前者深入,后者铺开。
四、判断是否为完全二叉树
判断是否为完全二叉树,我们怎么判断呢?
有人会想到用层数和节点个数来判断,但是它是完全二叉树吗?
我们可以想回顾一下,
传送门:数据结构之初识二叉树(1)——核心概念入门
1/ \
2 4\ \3 5例如这个就不是
所以我们可以还用队列实现,层序遍历,只要取到空,就跳出循环,看此时队列中剩下什么,如果只剩下空节点和非空节点,就是非完全二叉树,如果队列中剩下了空节点,就是完全二叉树。
代码实现:
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
// 遇到第一个空,就可以开始判断,如果队列中还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
if (TreeComplete(root))
{
printf("是完全二叉树\n");
}
else
{
printf("不是完全二叉树\n");
}
TreeDestory(root);
return 0;
}结果为非完全二叉树
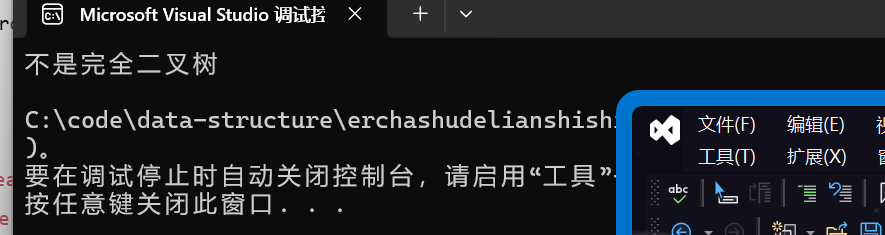
因为我们构造时没有构造成完全二叉树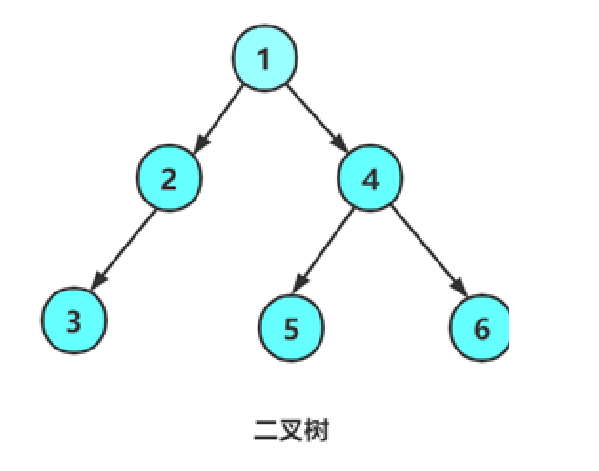
现在我们来构造成完全二叉树
只需要5,6节点删去或者再给2加个右节点(也就变成了满二叉树)就行啦
我们这里把5,6删去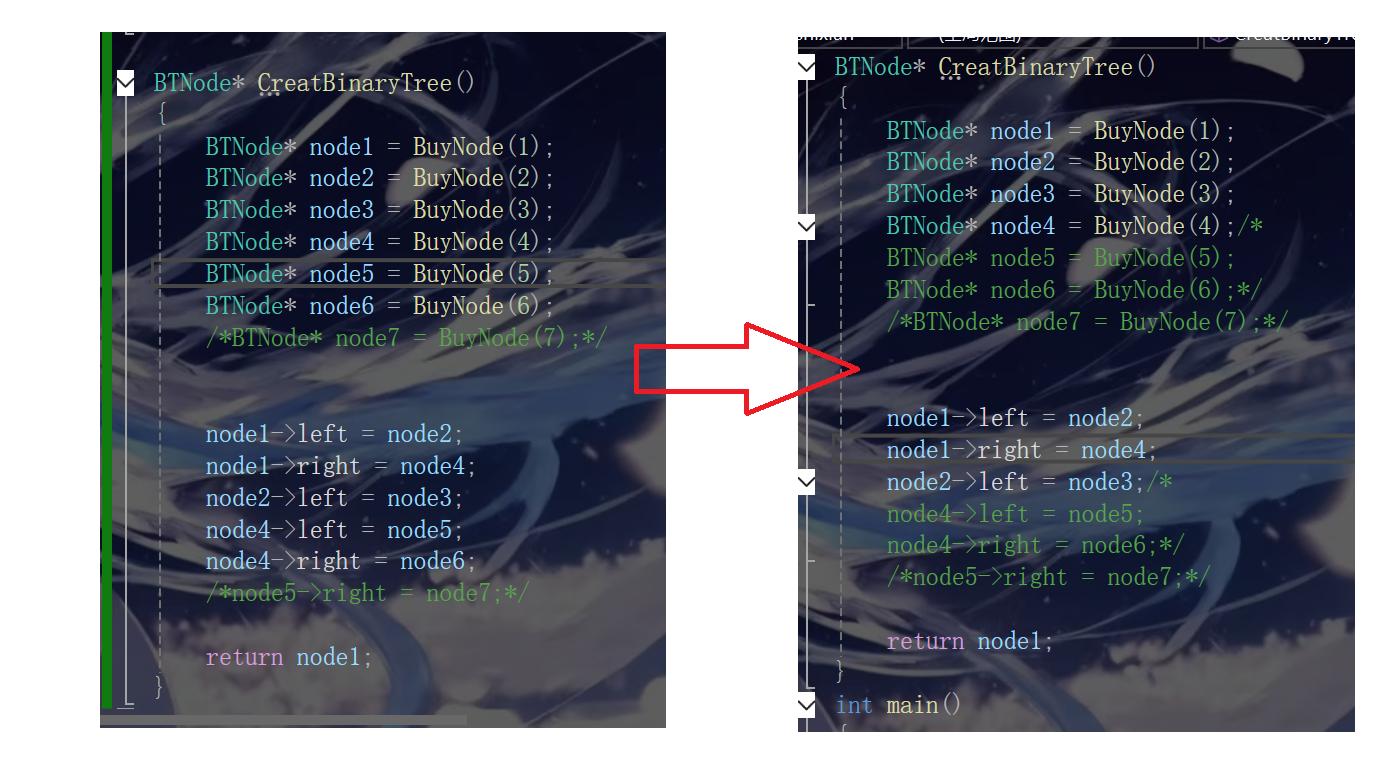
结果
正确实现
五、总代码(包括队列的代码)
队列相关代码
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<stdbool.h>#include<assert.h>typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType val;}QNode;typedef struct Queue{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;}Queue;void QueueInit(Queue* pq);void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);// 队尾插入void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);// 队头删除void QueuePop(Queue* pq);// 取队头和队尾的数据QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);int QueueSize(Queue* pq);bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//// 队尾插入//void QueuePush(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail, QDataType x);//// 队头删除//void QueuePop(QNode** pphead, QNode** pptail);Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
// 队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
// 队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size != 0);
/*QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;*/
// 一个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else // 多个节点
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}二叉树
Tree.h
#pragma once
#include"Queue.h"
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedef int BTDataType;typedef struct BinaryTreeNode{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;}BTNode;//前序遍历void PerOrder(BTNode* root);//中序遍历void InOrder(BTNode* root);//后序遍历void PostOrder(BTNode* root);//二叉树结点个数 int TreeSize(BTNode* root);//void TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize);//二叉树叶子结点个数 int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);//二叉树第k层结点个数 int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);//二叉树的高度int TreeHeight(BTNode* root);//二叉树查找值为x的结点 BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);// 二叉树销毁void TreeDestory(BTNode** root);//层序遍历void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root);// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root);Tree.c
#include"Tree.h"
//前序遍历
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
//二叉树结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//二叉树叶子结点个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left)
+ TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
// 子问题
return TreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1)
+ TreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
//二叉树的高度
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ?
leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
// 二叉树销毁
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
//// 二叉树销毁
//void TreeDestory(BTNode** root)
//{
// if (*root == NULL)
// {
// return;
// }
// TreeDestory(&((*root)->left));
// TreeDestory(&((*root)->right));
// free(*root);
// *root = NULL;
//}
#include"Queue.h"
//层序遍历
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
// 遇到第一个空,就可以开始判断,如果队列中还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
// 如果有非空,就不是完全二叉树
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}test.c
#include"Tree.h"
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);/*
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);*/
/*BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);*/
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;/*
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;*/
/*node5->right = node7;*/
return node1;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
/*printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));
printf("%d\n", TreeSize(root));*/
/*printf("%d\n", TreeLeafSize(root));
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);
printf("%d\n", TreeLevelKSize(root, k));
printf("%d\n", TreeHeight(root));
BTNode* find = TreeFind(root, 6);
if (find)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");
BTNode* fin = TreeFind(root, 7);
if (fin)
{
printf("找到了\n");
}
else
printf("没找到\n");*/
/*TreeLevelOrder(root);*/
if (TreeComplete(root))
{
printf("是完全二叉树\n");
}
else
{
printf("不是完全二叉树\n");
}
TreeDestory(root);
return 0;
}六、结束语
嗨ヾ(✿゚▽゚)ノ,本篇到这里就结束啦,相关知识传送门已经放在开头啦,主要讲了二叉树链式结构功能的实现,以及深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS),我们对树的讲解到这里就完美结束啦,但是我下一篇为大家准备了一些题目进行检验和巩固,(*❦ω❦)期待下一篇与大家相见,欢迎大家在评论区进行建议和讨论,我们下一篇再见啦!